Herbal Turmeric Help for Multiple Sclerosis

Multiple sclerosis, often referred to as MS, is a chronic autoimmune disease of the central nervous system. It is the most common neurological disorder among young adults in Westernized countries. In 30% of people with MS, the disease can mean permanent disability, including being wheelchair bound. MS is also associated with increased risk for other conditions, such as erectile dysfunction. (iv.3, 131, 132)
The causes and development of MS are not completely understood. However, genetics and environmental factors, including diet, can impact the risk of developing the condition. (iv.3, 131, 133)
The good news is that adding the turmeric to your diet could actually help protect you from MS. An antioxidant spice, turmeric also has potent anti-inflammatory compounds — especially curcumin. Studies suggest that turmeric and its compounds can relieve and reduce the inflammatory conditions that contribute to the disease. (iv.3, 131, 133, 134)
I'VE HEARD THAT SOME ANTIOXIDANTS CAN MAKE SYMPTOMS WORSE AND SLOW DOWN RECOVERY AFTER AN ACTIVE EPISODE OF MS. IS THIS TRUE?
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory flavonoids and other compounds are commonly found in many plants, including fruits, vegetables, and grains. In one animal study, researchers pretreated immune system cells with isolated compounds and transplanted them into mice. Compounds tested were apigenin, curcumin, fisetin, hesperitin, luteolin, morin, and quercetin. (iv.136)
The antioxidant flavonoids surprisingly increased the time it took to recover after an active phase of MS symptoms. This is relevant to turmeric because it contains three of the tested compounds: curcumin, quercetin, and fisetin. The longest delay in recovery was seen with morin, quercetin, and hesperitin. In two of the flavonoids (quercetin and hesperitin) symptoms of MS were more severe during the active phase. The study authors did note, however, that curcumin was beneficial and reduced recovery times. (iv.136)
On the other hand, many studies (including some conducted by the researchers involved in the one mentioned here) contradict the negative findings on the antioxidants. Evidence from clinical research on other neurodegenerative conditions show the benefits of many of these plant compounds. (iv.136, 138)
In addition, results of two later studies conducted on blood samples from human MS patients showed that quercetin and luteolin (separately) significantly regulated the inflammatory immune system response. The authors of the study on luteolin noted the difference in results between their research and the study mentioned above may have been the type of substance used to induce MS in the animal model. (iv.3, 136, 138)
How Does Multiple Sclerosis Damage the Brain?
In very basic terms, in MS over-activated immune system cells cause chronic inflammation. Excess free radicals are a sign of oxidative stress, which damages nerve tissue. The plaques in the brain that are a sign of active MS are actually lesions. They represent areas of injury in the brain where this inflammatory damage is occurring. (iv.3, 131, 135)
The cascade of destructive activities in MS includes: (iv.3, 131, 135)
- Demyelination: A process that strips the myelin sheath that protectively coats the ends of neuron brain cells. Demyelination also destroys the brain cells that make myelin.
- Free radical damage to mitochondria: The organelles in cells responsible for converting the food we eat into energy. Damaged mitochondria severely reduce levels of cell energy. They also worsen the chronic inflammatory conditions by creating more free radicals.
- Toxic accumulation of iron: Released by the destruction of the myelin sheath and myelin-producing cells, which contain iron.
- Damage to the blood-brain barrier: Permits more inflammatory immune system cells to cross the barrier and attack neuron brain cells.
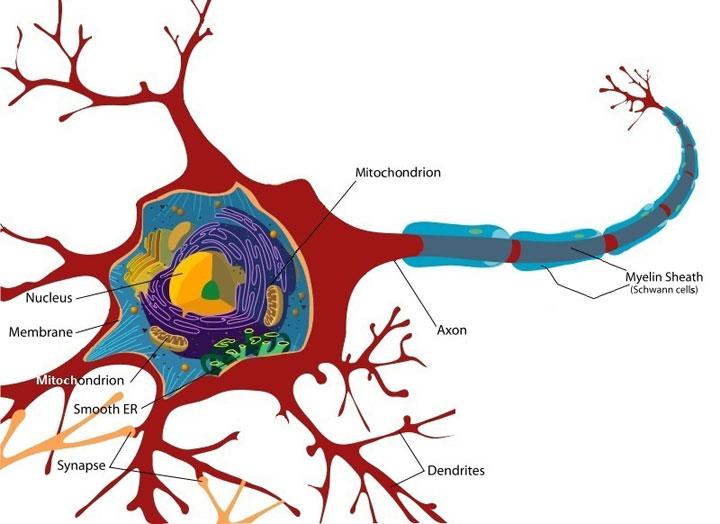
Neuron
What Happens When Multiple Sclerosis Progresses?
During the initial stage of MS, patients have periods of time where the disease is inactive between relapses. Eventually MS changes to a progressively worsening condition. This typically occurs between the ages of 40 and 50, and coincides with age-related excess iron build-up in the brain. (iv.3, 102, 131)
In the progressive stage of MS, there is actually less active inflammation. Experts suggest that the combination of aging with accumulated iron left from myelin and cell destruction could explain why the lesions continue to expand even though inflammation is reduced. (iv.3, 102, 131)
As the disease progresses, the parts of the nerve cells beyond the myelin sheath are affected as well. Eventually the neuron brain cells are destroyed. (iv.3, 102, 131)
How Can Turmeric Help with MS?
Research suggests that many of the compounds in turmeric may help block the inflammatory damage associated with MS. The studies on turmeric compounds have mostly been conducted on curcumin, the main (non-flavonoid) compound in turmeric, and have shown positive benefits. For example, in an animal model of multiple sclerosis, mice given curcumin in their diet during an active episode of the disease recovered faster than the untreated control group. Pretreatment with curcumin also resulted in faster recovery times. Other animal studies show that curcumin treatment reduces the severity of MS symptoms. (iv.134, 136, 137)
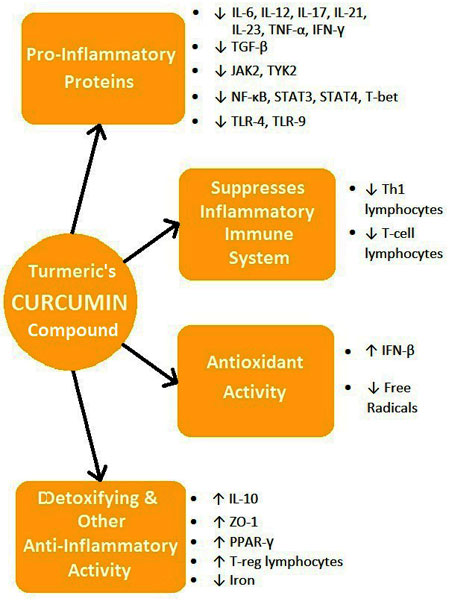
Curcumin is able to cross the blood-brain barrier and get into the areas affected by multiple sclerosis. Evidence suggests that this ability, as well as its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, could provide additional benefit to conventional MS treatments. (iv.1, 3, 6, 87, 88, 115, 134, 137, 139)
Lab and animal research demonstrate curcumin's effects against the inflammatory proteins and immune system cells that cause demyelination and brain cell damage. Curcumin also: (iv.1, 3, 6, 87, 88, 115, 134, 137, 139)
- Promotes antioxidant and anti-inflammatory proteins.
- Gets rid of free radicals.
- Helps repair the blood brain barrier.
- Helps reduce the toxic accumulation of iron in the brain.
Join the 1000s of People Who Are Discovering the Benefits of Turmeric.

Healthceuticals® Turmeric Curcumin Complex
100% Certified
Organic ingredients
- Organic Turmeric Extract - standardized to 95% curcuminoids.
- Organic Whole Turmeric - provides full spectrum antioxidant, anti-inflammatory turmeric benefits, including turmerones and numerous vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients
- Organic Black Pepper Extract - standardized to 95% piperine; dramatically enhances bioavailablity.
- Organic Phospholipids - markedly improve absorption.
- Organic Ginger - works synergistically with turmeric to provide more powerful benefits.
- Absolutely FREE of potentially harmful additives and fillers such as magnesium stearate.




