Natural Herbal Help for Encephalopathy
Somewhere between acute brain injury and chronic dementia is the type of brain disease and damage referred to as encephalopathy. There are several different types of encephalopathy. They types are diagnosed based on what causes them and their symptoms. (iv.4, 12-13, 111-112)
Studies suggest that the turmeric compound curcumin could help relieve the symptoms associated with certain kinds of encephalopathy, including: (iv.4, 12-13, 111-112)
- Diabetic and hepatic encephalopathy
- Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
- Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease
Although these types all differ in cause, all four feature some loss of thinking and/or memory brain function. Turmeric's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in protecting brain cells and preventing or restoring cognitive function may make it a natural herbal remedy for encephalopathy. (iv.4, 12-13, 111-112)
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
Wernicke-Korsakoff is considered to be a potentially reversible dementia syndrome. It is caused by a deficiency in one of the essential B vitamins (thiamine). (iv.70, 113)
Who's at Risk for Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome?
Three factors increase the risk of this syndrome: (iv.70, 113)
- Alcoholism. Because alcohol blocks the ability to absorb thiamine, chronic high levels of alcohol consumption increases the risk of developing thiamine deficiency. This may make those suffering from alcoholism more susceptible to developing Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
- Age and poor nutrition. Another group at risk of developing this Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is elderly people with poor nutrition (with or without alcoholism). By some estimates, up to 40% of elderly patients are moderately or severely thiamine-deficient.
Symptoms may mimic those of Alzheimer's disease, and include: (iv.111-113)
- Confusion
- Memory loss
- Inability to move eyes
Mad Cow Disease
Referred to as the human form of mad cow disease, Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease is a spongiform encephalopathy caused by infectious prion protein agents. Only one type of CJD is thought to possibly come from consuming meat contaminated with nervous tissue of a cow infected with mad cow disease, and it typically occurs in young adults. Other types arise from: (iv.114-117)
- Heredity. A genetic mutation of the gene that forms prion proteins.
- Medical exposure. Cases have developed from accidental exposure to contaminated surgical instruments, corneal or membrane transplants from an infected donor, or injections of infected human growth hormones.
However, the vast majority of cases are of unknown origin and the average age of onset is in the mid-sixties. (iv.115-117)
Unlike bacteria or viruses, infectious prions do not replicate themselves when they infect a person. Instead, they convert existing prion proteins (Prc) (mostly located in the brain and neural tissue) to disease-causing forms (Prsc). Other features of Prsc prions that make them different than the normal Prc prions include: (iv.115-117)
WHY IS CJD CALLED A SPONGIFORM ENCEPHALOPATHY?
Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease is similar to Alzheimer's disease in symptoms of dementia. Areas of degeneration in the brain also show the formation of amyloid-beta plaques. (iv.115)
However, in CJD areas of the brain also show vacuoles surrounding the plaques. Vacuoles are holes in the brain left after the diseased neuron cells die. They resemble the holes in a sponge — hence the term spongiform. (iv.102, 118)
- Prsc are misfolded.
- They are resistant to normal breakdown by protease enzymes.
- Prsc converts normal Prc from an alpha helix shape to an amyloid-beta version that tends to form toxic clumps.
Symptoms are similar to Alzheimer's disease except they rapidly progress to severe dementia and death within 6 months to 3 years after symptoms first appear. However, CJD also includes loss of coordination because the cerebellum area of the brain that controls muscles and movement is involved. The most common symptoms include: (iv.114-117)
- Behavioral changes
- Dementia
- Muscle twitching and spasms
Diabetic Encephalopathy
Elevated levels of glucose in cells can cause direct damage and cell death in brain neurons. When neurons in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus regions of the brain are affected, it results in symptoms that include impaired learning and memory. (iv.12)
At the cellular level, diabetic encephalopathy is similar to Alzheimer's disease. Dysfunctional cell activities include: (iv.12)
- Nitrogen-based (NO) free radicals.
- High levels of inflammatory transcription factor and cytokine proteins.
- Reduced levels of the body's own natural antioxidants.
- Increased activity of acetylcholinesterase. This is the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine, a neurotransmitters essential for cognitive function and memory.
NITRIC OXIDE (NO) & THE BRAIN
Nitric oxide (NO) is a highly reactive free radical. It is produced by a group of enzymes called nitric oxide synthases (NOS or iNOS). Under normal conditions, NO behaves as a neurotransmitter and antimicrobial substance. (iv.102)
When the brain is in a chronic inflammatory state, overstimulated astrocyte immune system cells release lots of NOS. The high levels of NO they produce are extremely toxic to neurons. Studies show that curcumin can suppress dangerous levels of NOS and NO free radicals. (iv.102)
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is an inflammatory condition in the brain, but it begins in the liver. In fact, it is actually considered a complication of acute or chronic liver failure. Hepatic encephalopathy is caused by toxins (e.g., ammonia and excess manganese) which the liver fails to remove from the body. The toxins damage neuron brain cells and functioning. The origin of this type of liver malfunctioning is an underlying liver condition (e.g., cirrhosis, acetaminophen poisoning, and hepatitis C). (iv.119)
Hepatic encephalopathy is a serious condition that can be fatal. Symptoms include: (iv.119)
- Sleep disturbances
- Behavioral changes
- Impaired cognition
- Fine motor coordination problems
- Coma
Acute liver failure causes significant swelling in brain astrocyte cells. Changes at the cellular level in hepatic encephalopathy are similar to neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson's disease. They include: (iv.8, 32, 119)
- Overactive and overexcited immune system brain cells that cause chemical and antioxidant imbalances.
- Damaged and dysfunctional mitochondria and decreased cell energy.
- Increased levels of nitrogen (NO) and oxygen-based free radicals.
- Disturbances in calcium levels.
- Stimulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine proteins.
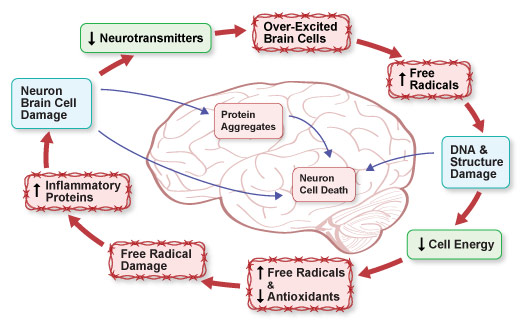
Figure IV.20: Inflammatory Conditions in Hepatic Encephalopathy
Helpful Turmeric Compounds
Turmeric contains many compounds beneficial to the brain. These include nutrients such as thiamine and lyphenol compounds (e.g., curcumin, quercetin, and resveratrol). Studies suggest their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties can relieve the inflammation and prevent free radical damage found in encephalopathy. In addition, turmeric and curcumin could help resolve underlying conditions that cause encephalopathy, such as diabetes and liver conditions. (iv.34, 36, 41)
| CONDITION | EFFECT OF CURCUMIN |
|---|---|
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (WKS) |
In an animal model of WKS, daily treatment with oral curcumin for 8 days helped improve cognitive learning. Pretreatment with curcumin in this study also improved spatial memory. It produced better results than curcumin given after WKS was induced. (iv.14) |
Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease; Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSES); Prion Diseases |
Lab studies show that curcumin stops the conversion of normal prion proteins to the protease-resistant form. (iv.15) An animal study was conducted comparing various treatment drugs for prion diseases. Mice treated with low doses of curcumin (50 mg/kg of body weight) had small but statistically significant longer survival times than those treated with dapsone, ibuprofen, and the tetracycline-antibiotic minocycline. Results were similar to the drug memantine. Very high doses of curcumin (500 mg/kg of body weight) had no effect on survival time. (iv.16) |
Diabetic Encephalopathy |
In an animal study, rats with diabetic encephalopathy were treated daily with curcumin (dosages of 60 mg/kg of body weight). Curcumin significantly reduced acetylcholinesterase enzyme activity, inflammation, and free radical oxidative stress. These changes resulted in improved cognitive function. (iv.12) |
Hepatic Encephalopathy |
In an animal model of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy, 3 dosages of curcumin (100 mg/kg of body weight) protected against free radical damage in the hippocampus section of the brain. It did so by stimulating natural antioxidants while reducing levels of free radicals. (iv.13) |
Join the 1000s of People Who Are Discovering the Benefits of Turmeric.

Healthceuticals® Turmeric Curcumin Complex
100% Certified
Organic ingredients
- Organic Turmeric Extract - standardized to 95% curcuminoids.
- Organic Whole Turmeric - provides full spectrum antioxidant, anti-inflammatory turmeric benefits, including turmerones and numerous vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients
- Organic Black Pepper Extract - standardized to 95% piperine; dramatically enhances bioavailablity.
- Organic Phospholipids - markedly improve absorption.
- Organic Ginger - works synergistically with turmeric to provide more powerful benefits.
- Absolutely FREE of potentially harmful additives and fillers such as magnesium stearate.




